My Specialties & Services
Endoscopy
Upper Endoscopy (EGD)
Read More
Upper endoscopy, also known as EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy), is a procedure that involves the use of a flexible tube with a camera to examine the upper digestive system, including the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The procedure is used to diagnose and treat conditions such as ulcers, inflammation, and cancer in the upper digestive tract.
Colonoscopy
Read More
Colonoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the colon to examine its lining for abnormalities, such as polyps or cancer. It is a vital tool for the early detection and prevention of colorectal cancer, which is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Colonoscopy is generally considered safe and effective and can be performed as an outpatient procedure with sedation. By detecting and removing polyps before they turn into cancer, colonoscopy can save lives and help maintain good digestive health.
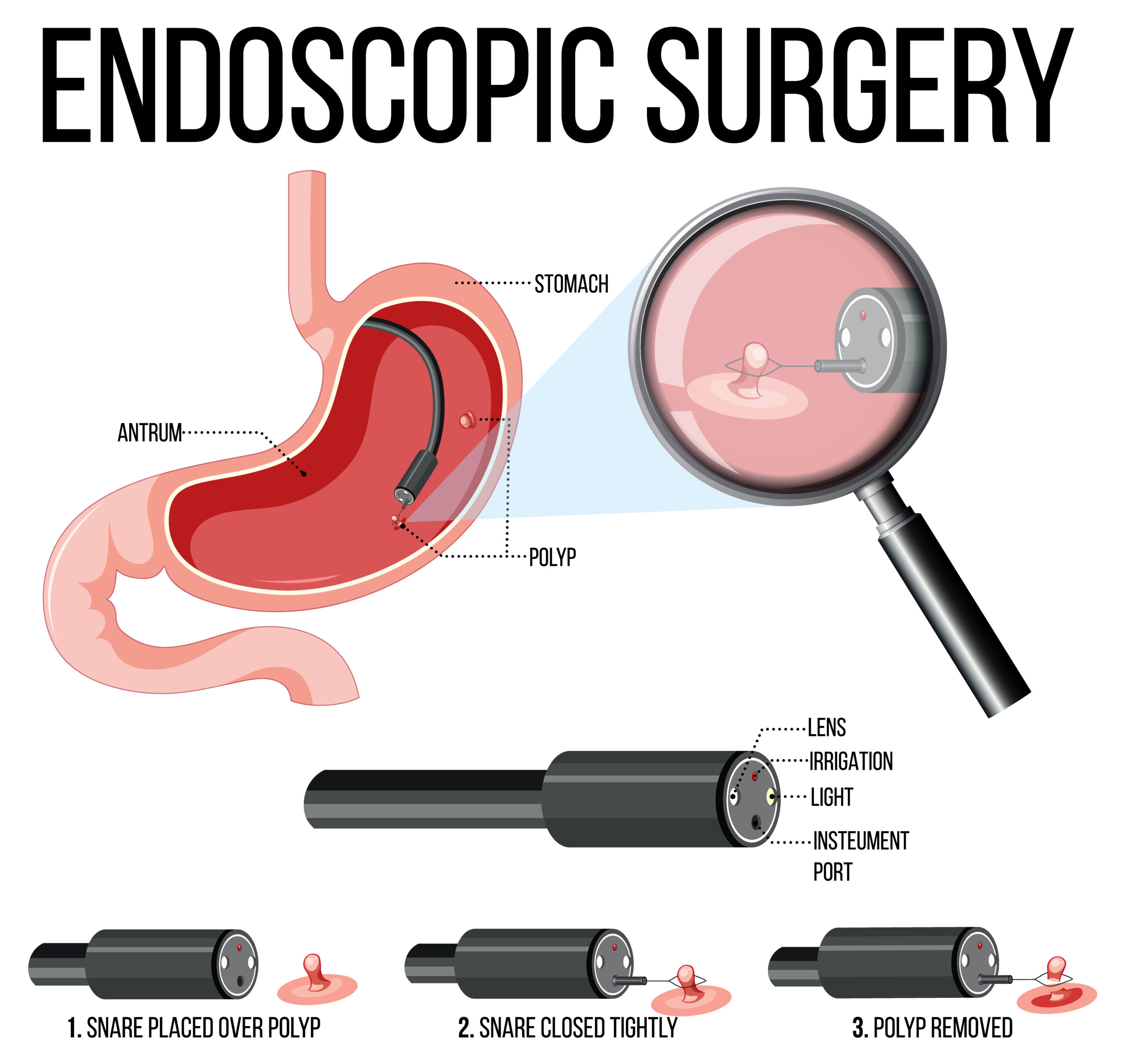
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR: large tumor removal)
Read More
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR) is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a flexible tube with a specialized tool to remove large tumors in the digestive system, such as the esophagus, stomach, or colon. EMR is a highly effective alternative to surgery for removing tumors that have not spread deeply into the layers of the digestive tract. The procedure involves injecting a solution under the tumor to lift it away from the surrounding tissue, and then using a snare to cut and remove the tumor. EMR is a safe and effective option for treating tumors that might otherwise require more invasive surgery, and it has a high success rate in preventing cancer recurrence. EMR needs additional training and only a few Gastroenterologists can perform this procedure.
Capsule Endoscopy (Pill Camera)
Read More
Capsule Endoscopy, also known as Pill Camera, is a non-invasive procedure that involves swallowing a small capsule equipped with a camera and a light source, which then takes pictures and videos of the digestive system as it passes through. The capsule is designed to travel naturally through the digestive tract, providing a detailed view of the small intestine, which is not easily accessible by other endoscopic techniques. The images captured by the camera are transmitted to a recorder worn on the patient’s waist, which is then reviewed by a gastroenterologist. Capsule Endoscopy is a safe and painless procedure that allows for the detection and diagnosis of conditions such as Crohn’s disease, ulcers, and tumors in the small intestine, without the need for invasive procedures.
Sigmoidoscopy
Read More
Sigmoidoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure that involves the use of a flexible tube with a camera to examine the rectum and lower part of the colon. Unlike colonoscopy, which examines the entire colon, sigmoidoscopy only examines the left side of the colon. The procedure is typically performed to screen for colon cancer, identify the cause of rectal bleeding or abdominal pain, or monitor the progress of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Sigmoidoscopy is a relatively quick and safe procedure that can be performed without sedation, and it can help diagnose and treat conditions of the lower digestive tract.
Hemorrhoid Banding
Read More
Hemorrhoid banding is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat hemorrhoids, which are swollen veins in the anus or lower rectum. The procedure involves placing a small rubber band around the base of the hemorrhoid, which cuts off its blood supply and causes it to shrink and eventually fall off. Hemorrhoid banding is a safe and effective treatment option for grade I to III internal hemorrhoids, which are not responsive to conservative treatments such as dietary changes and topical creams. The procedure can be performed in the office and does not require anesthesia or hospitalization, and it has a high success rate with minimal pain and recovery time.
Esophageal pH Test
Read More
Esophageal pH test is a diagnostic procedure that measures the amount of acid that flows into the esophagus from the stomach over a 24-hour period. The test involves placing a small, flexible tube with a sensor into the esophagus through the nose or mouth, which measures the acidity levels in the esophagus. The test is typically performed to diagnose gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is a condition in which stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing heartburn, chest pain, and other symptoms. The esophageal pH test is a safe and minimally invasive procedure that provides valuable information about the severity of acid reflux, and can help guide treatment decisions.
Advanced Endoscopy (ERCP and EUS)
Read More
- Advanced endoscopy is a specialized field that includes two important procedures: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). ERCP is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure used to examine the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, while EUS uses an ultrasound probe to visualize the digestive tract and surrounding organs. These procedures are typically performed to diagnose and treat conditions such as gallstones, pancreatic cancer, or biliary tract obstruction, and require specialized training and expertise from a gastroenterologist. Both ERCP and EUS are minimally invasive, safe, and effective diagnostic and therapeutic tools that can help diagnose and treat a variety of gastrointestinal conditions.
- Advanced endoscopy is a critical tool in the diagnosis and treatment of many gastrointestinal conditions. This field includes two specialized procedures: endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). ERCP is a diagnostic and therapeutic procedure that can be used to examine the bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, remove gallstones, or place stents to improve bile or pancreatic flow. EUS, on the other hand, uses an ultrasound probe to visualize the digestive tract and surrounding organs, and can be used to diagnose and stage cancers of the esophagus, stomach, pancreas, and rectum. Both ERCP and EUS are performed by a gastroenterologist with additional training in advanced endoscopy, and are safe, minimally invasive, and effective diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
About Endoscopy
Endoscopy is a medical procedure that involves using an endoscope, which is a flexible tube with a camera and light source attached to it, to examine the inside of the body. The endoscope is inserted through a natural opening in the body, such as the mouth, nose, or anus.
During an endoscopy, the doctor can see images of the inside of the body on a screen and can use special instruments attached to the endoscope to take biopsies (small samples of tissue) or remove polyps or other abnormal growths. This can help diagnose and treat a variety of medical conditions.
GI endoscopy can be used to examine different parts of the body, such as the digestive system (esophagus, stomach, and intestines).
Endoscopy is a minimally invasive procedure, which means that it can often be performed without the need for major surgery or a long recovery period. It is usually performed under sedation or anesthesia, and patients can usually return home the same day. However, like any medical procedure, there are some risks associated with endoscopy, such as bleeding or infection, and patients should discuss these risks with their doctor before undergoing the procedure.