My Specialties & Services
Liver Diseases (Hepatology)
Abnormal Liver function test (LFT)
Read More
Abnormal liver function tests (LFTs) can indicate liver disease or other medical conditions. LFTs measure certain enzymes and substances in the blood that are produced by the liver. Causes of abnormal LFTs include viral infections, alcohol abuse, fatty liver disease, autoimmune disorders, medications, and other medical conditions. Further evaluation may be necessary to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Hepatitis (A, B, C, D, E)
Read More
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, which can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral infections, alcohol abuse, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications or toxins. There are several types of viral hepatitis, including hepatitis A, B, C, D, and E.
Hepatitis A is typically transmitted through contaminated food or water and is usually a self-limited illness that does not lead to chronic infection.
Hepatitis B, C, and D are usually spread through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids and can lead to chronic infection, liver damage, and an increased risk of liver cancer.
Hepatitis E is similar to hepatitis A and is typically spread through contaminated food or water.
Treatment for hepatitis depends on the underlying cause and severity of the disease, and may include antiviral medications, lifestyle modifications, and other supportive measures to manage symptoms and prevent complications. Vaccines are also available to prevent hepatitis A and B infections.
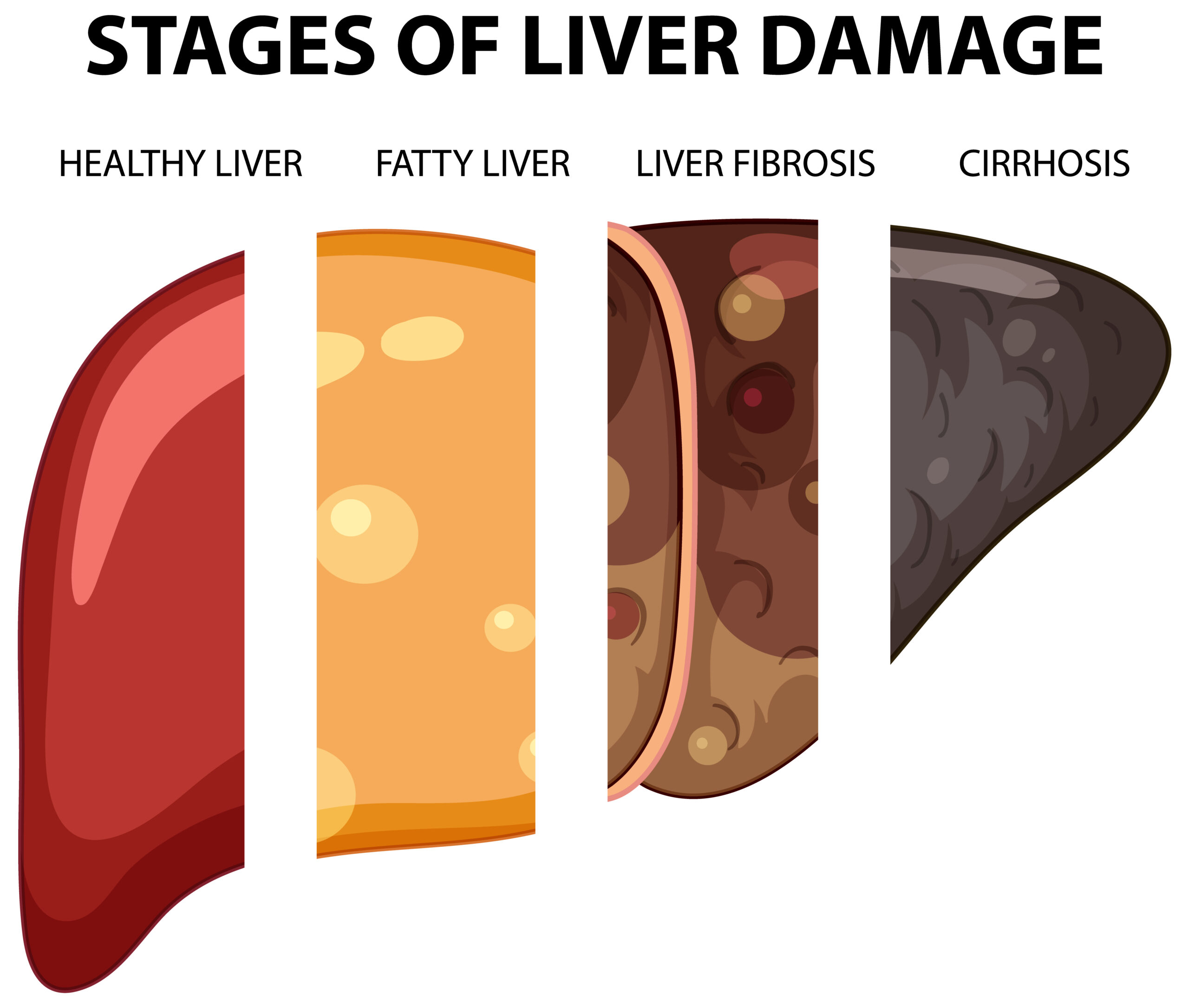
Cirrhosis
Read More
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease that occurs when healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue, leading to progressive liver damage and dysfunction. It can be caused by a variety of factors, including chronic viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, fatty liver disease, autoimmune disorders, and certain medications or toxins.
Symptoms of cirrhosis may include fatigue, weakness, abdominal pain, jaundice, and fluid accumulation in the abdomen or legs. Complications of cirrhosis can include portal hypertension, which can lead to varices and gastrointestinal bleeding, and hepatic encephalopathy, which can cause confusion, memory problems, and coma.
Treatment for cirrhosis focuses on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and slowing the progression of the disease. This may include lifestyle modifications, medications to manage symptoms or complications, and in some cases, liver transplantation.
Liver Failure
Read More
Liver failure is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the liver is unable to perform its normal functions due to severe damage or disease. It can be acute, occurring rapidly over a few days or weeks, or chronic, developing gradually over months or years.
Acute liver failure is most commonly caused by drug toxicity, viral hepatitis, or autoimmune disorders, while chronic liver failure is typically the result of long-term liver disease, such as cirrhosis.
Symptoms of liver failure may include jaundice, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, confusion, and in severe cases, coma. Treatment for liver failure may include supportive care to manage symptoms and prevent complications, as well as liver transplantation in some cases.
Prevention of liver failure involves avoiding excessive alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding exposure to toxins, and getting vaccinated for viral hepatitis. Early detection and treatment of liver disease can also help prevent the development of liver failure.
Fatty Liver
Read More
Fatty liver, also known as hepatic steatosis, is a condition in which excess fat accumulates in the liver cells. It is a common condition that can be caused by various factors, including obesity, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and excessive alcohol consumption.
Most people with fatty liver have no symptoms and the condition is often discovered incidentally during routine blood tests or imaging studies. In some cases, fatty liver can progress to a more serious condition called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which can cause liver inflammation, fibrosis, and eventually lead to cirrhosis and liver failure.
Treatment for fatty liver involves addressing the underlying cause, such as weight loss and lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and exercise. In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help control blood sugar, cholesterol, or other conditions that contribute to fatty liver. It is important to seek medical attention and follow recommended treatments to prevent the progression of fatty liver to more serious liver disease.
Liver Mass
Read More
A liver mass refers to an abnormal growth or lump in the liver tissue that may be either benign or malignant. Common causes of liver masses include liver cancer, such as hepatocellular carcinoma, or metastatic cancer, which is cancer that has spread to the liver from another part of the body.
In some cases, liver masses may be discovered incidentally during routine imaging studies, while in other cases, patients may experience symptoms such as abdominal pain, nausea, or jaundice.
The treatment options for liver masses depend on several factors, including the size and location of the mass, whether it is benign or malignant, and the overall health of the patient. Treatment may involve surgery to remove the mass, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of these approaches.
It is important to seek prompt medical attention if you have any symptoms or concerns related to liver masses.
Liver Cyst
Read More
A liver cyst is a fluid-filled sac that forms in the liver tissue. Although common, they are usually not cancerous and often do not cause any symptoms. However, if they grow in size or cause discomfort, treatment options such as draining or surgical removal may be recommended. Multiple cysts may indicate a genetic condition, and genetic testing and further evaluation may be necessary. It’s important to seek medical attention if you have any symptoms or concerns about liver cysts. Your doctor can help determine the best management plan based on the size, location, and overall health of the patient.
About Liver Diseases (Hepatology)
Liver diseases, also known as hepatology, is a specialized area of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions that affect the liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas. The liver is an essential organ that performs vital functions such as detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of bile, which helps in the digestion of fats.
Hepatologists are medical professionals who specialize in the study and treatment of liver diseases. They are trained to diagnose and manage a wide range of liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver cancer, autoimmune liver disease, and metabolic liver disease, among others. Hepatologists use a variety of diagnostic tools, including blood tests, imaging studies, and liver biopsies, to identify and diagnose these conditions.
Once a diagnosis is made, hepatologists may recommend a range of treatments, depending on the severity and type of liver disease. Treatment options can include medications, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgery or liver transplantation.
Hepatology is an important area of medicine, as liver diseases can have serious consequences if left untreated. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for the best possible outcomes, and hepatologists play a critical role in providing specialized care for patients with liver diseases.